From about 1000 BC to 333 BC, when Alexander the Great landed in the Nile Delta, Egypt struggled to maintain its independence.
Unable to unify under one king, Egypt was caught in the ongoing power struggle between the many other civilizations flourishing in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia at the time.
But this lack of independence does not mean that Egypt did not impact the history of this period. In fact, much of what happened during this era, known as the Late Period, set the stage for the momentous change that was set to take place in the ancient world in the 4th century BC.
Assyrian Invasion
The Assyrians, who originated from what is now modern-day Iraq, rose to power in the ancient world. They targeted Egypt due to its many riches, and eventually reached and sacked Thebes, the long-time capital of Egypt, in c. 663 BC.
The Saite Dynasty
From about 1000 BC to 800 BC, the ancient world suffered through what is known as the Late Bronze Age Collapse. War with invading tribes as well as challenging environmental conditions made life difficult. Political unity escaped Egypt and also the many other civilizations existing at the time.
Towards the end of this period, the Assyrians, who originated from what is now modern-day Iraq, rose to power in the ancient world. They targeted Egypt due to its many riches, and eventually reached and sacked Thebes, the long-time capital of Egypt, in c. 663 BC.
This created an opening in Egypt for a new ruler, and the kings of the city of Sais jumped on the opportunity. They established the 26th Dynasty of Egypt, also known as the Saite Dynasty.
The creation of this dynasty briefly restored political stability in Egypt and allowed progress to occur.
For example, during this time, the Egyptians began work on a canal to connect the Nile River to the Red Sea. When this was finished, it opened up significant trade routes with the East that would help Egypt return to power.
But the Saite Dynasty was short-lived. The Assyrians fell to the Persians, who were based out of modern-day Iran. Seeing the growing power in Egypt as a threat, they soon embarked on a campaign to conquer Egypt.
Persian Invasion
Persian rulers set their sights on Egypt and its fertile farmland. They succeeded under Cambyses in 525 BC, and Egypt became part of the Persian empire.
Persian Conquest and Rule of Egypt
The Persian Empire emerged onto the ancient scene thanks to the growth of a few small cities in northern Iran. But it soon became the ancient world’s most feared and powerful empire.
As it expanded throughout Asia, Persian rulers set their sights on Egypt and its fertile farmland. They succeeded under Cambyses in 525 BC, and Egypt became part of the Persian empire.
This was not the first time Egypt had been invaded and run by foreigners. But life under Persian rule was quite different than it had been during previous occupations.
Persia ruled through a system of satrapies, another name for provinces. Provincial governors, known as satraps, were in charge of carrying out the will of the Persian emperor.
In general, these satraps worked to oppress Egyptian culture and way of life. They moved against Egyptian religion by installing their own priests and building their own temple. They also imposed heavy taxes on the Egyptian people.
This created great resentment in Egypt towards Persia, and almost every time a new emperor rose in Persia, the Egyptians rebelled.
Not wanting to lose Egypt, new Persian leaders would send armies to quell these insurrections, meaning that war plagued Egypt during most of this time.
Unable to break free, the Egyptians were forced to accept Persian rule. But perhaps more importantly, they were forced to join the Persian army in its many wars of conquest throughout the ancient world.
This would end up having considerable consequences for both Persia and Egypt.
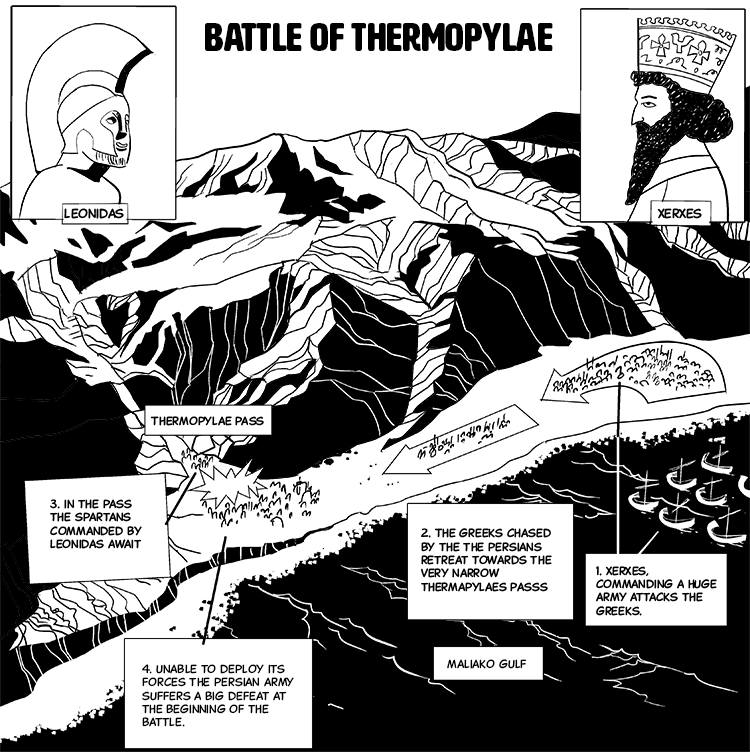
Battle of Thermopylae
The infamous Xerxes I launched one of the largest invasions the world had ever seen, only to be stopped at the Battle of Thermopylae.
The Greco-Persian Wars
At the height of the Persian Empire, it controlled all of Mesopotamia, as well as much of the lands in Egypt, Palestine, and modern-day Jordan and Syria. To the east, Persian influence extended almost to India.
But since conquerors are not usually known for their restraint, this was not enough. Starting with Darius I, the Persians set their sights on adding Greece to their empire.
Their first attempt failed with the Greeks winning the famous Battle of Marathon. Then, some ten years later, the infamous Xerxes I launched one of the largest invasions the world had ever seen, only to be stopped at the Battle of Thermopylae.
During all this war, the Persians relied heavily on the Egyptians. Egyptian soldiers and sailors were forced to fight on behalf of the Persians, and Egypt itself was used as a launching point for sea attacks on Greece.
Later, when Athens continued to fight in its efforts to expand its own power, several battles took place on Egyptian soil, with the Greeks hoping to undermine Persian influence there and topple the Persian empire.
Ultimately, these attempts failed. But this set the stage for what was to come, mainly the invasion of Alexander the Great.
Greek Invasion
Alexander the Great, the leader of the Greek kingdom of Macedon, stormed into Egypt in 333 BC with his armies. Less than one year later, he had defeated the Persians and made Egypt part of his growing empire.
The Rise of the Kingdom of Macedon
After a very brief period of independence, Egypt was once again incorporated into the Persian empire. But this time, occupation would not last long.
Alexander the Great, the leader of the Greek kingdom of Macedon, stormed into Egypt in 333 BC with his armies. Less than one year later, he had defeated the Persians and made Egypt part of his growing empire.
Egypt was one of the first territories Alexander targeted outside Greece. He did this not only because of the strategic importance of Egypt but also because of the role the Egyptians had played in the Greco-Persian Wars.
Alexander’s invasion was seen as a liberation, and it launched a new era in Egyptian history. During this time, Egypt regained its prominence in the world and became a center for trade and learning.
The Significance of the Late Period
While a somewhat dark time in Egyptian history, the Late Period was significant in that it reminded ancient leaders that they could not hope to grow their power without Egypt.
It also set the stage for Greek influence in Egypt, which also brought the Romans, the Greeks leading competitors, onto the scene.
From this position, Egypt continued to heavily influence world politics and contributed greatly to the development of world culture and civilization.
Written by Matthew Jones
Illustrated by Pablo Velarde Diaz-Pache